
In this case, we can see that curve gets steeper as the time increases, this means that the object is covering more distance in less time - or it is getting faster (accelerated movement). This is called an exponential curve, mathematically you will not deal with these this year, but we can talk about what it means without going into the mathematcs yet! You can do the two calculations to check if you like! (in both cases the change in y is zero, so the answer is zero) There is a 'flat' line, this means that the y co-ordinate (distance) is not changing, so the object is still - it's speed is zero m/s by calculating the gradient (pendiente) of the line.: Change in y/change in x - in this case (40-0)/(20-0) = +2 m/s.distance from the graph = 40m / time from the graph 20s So speed = 40/20 = 2 m/s.There is a straight 'upwards sloping line - this indicates that the distance and the time change in the same proportion ( a directly proportional relationship) we can calculate the speed in this section by two methods: In this case we can use the graph to see many things. The acceleration of a movement is the rapidity with which its velocity changes.

The accelerated movement is a movement in which velocity changes with time. The instantaneous speed of a moving object is the speed of the object at a particular instant. The average speed of a moving object is the displacement of the object divided into the time the object takes to cover a distance. For our purposes, as since we are not going to see vectors this year, we may interchange the terms speed and velocity. Speed has a different meaning than velocity, as speed is a scalar quantity and velocity is a vector quantity.

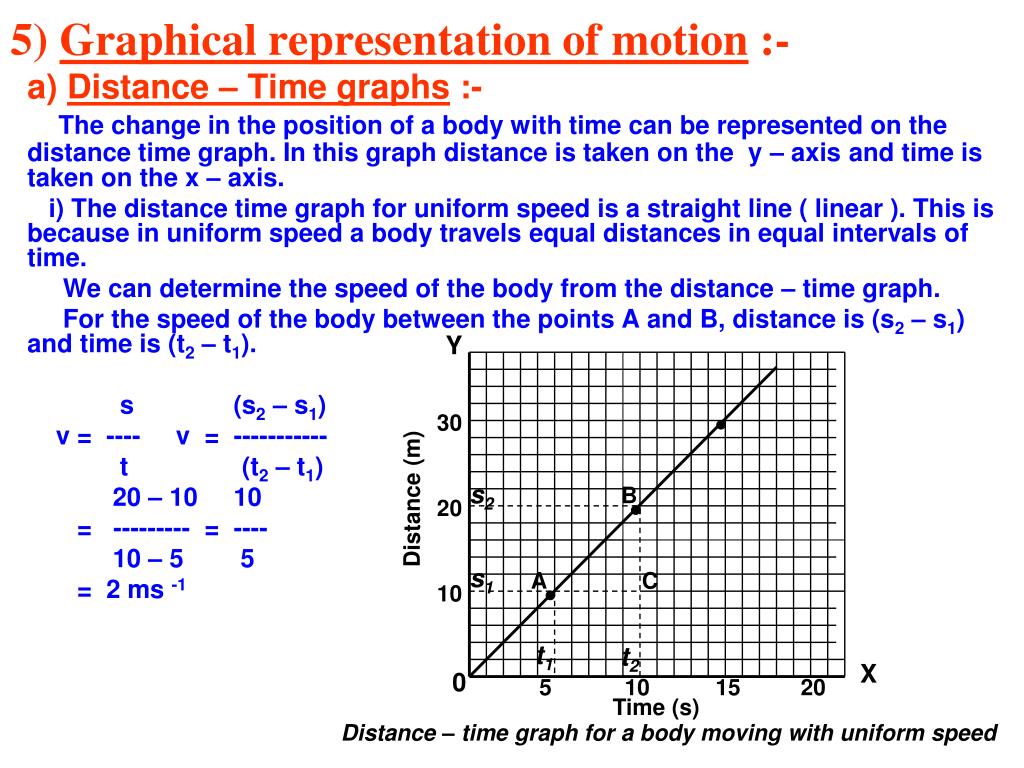
Motion is relative: the change of position is made with reference to a point we call a reference system.Speed time graph when the initial speed of the body is not zero.A movement is a body’s change of position with time. In a speed time graph of a body a straight line sloping downwards indicates retardation. The distance travelled by a moving body in a given time can be calculated from speed time graph.ĭistance travelled = Area of triangle POQ In a speed time graph the acceleration is given by slope of the graph. The value of acceleration from speed time graph of moving body can be calculated as:Ī = Change in speed or velocity / Time taken Speed time graph for a uniformly changing speed will be a straight line. (1) When a body moves with uniform acceleration ,its speed changes by equal amount in equal intervals of time. (2) Speed-time graph when speed changes at uniform rate (uniform acceleration) The velocity time graph of an object moving with constant velocity is a straight line parallel to time axis. We can find the distance travelled by a body in a given time from speed-time graph.ĭistance travelled = Area of rectangle OABC (a) Speed time graph for a body moving with constant speed(no acceleration) is a straight line parallel to time axis. Speed – Time or velocity – Time Graphs (1) Speed-time graph when speed remains constant


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
